School of Medicine Annual Enrollment 105 / Period of Attendance 6years
◆ Educational Purposes
Approaching health and environments of working people through the eyes of medical science, occupational health physicians play extremely important roles for several reasons, including their support for the development and revitalization of industry. The School of Medicine trains occupational health physicians with rich humanity that enables them to consider medical science more deeply and from wider perspectives in industrial society.
◆ Diploma Policy
The Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, the University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Japan, confers a graduation certificate in Medical Science on students who have: 1) understood the objectives and mission of the university, which “conducts educational research related to medical science, nursing science and other healthcare sciences, contributes to the promotion of these sciences that are elevant to the working environment and workers’ health, and develops medical professionals in these fields”; 2) acquired the knowledge, skills and attitude that are essential to a physician in the course terms or longer, as prescribed by the university; 3) acquired the qualities and abilities necessary to take a central leadership role in the research and practical fields of occupational health medicine; 4) completed the number of course hours required for graduation and receive the course completion certificate; 5) passed the comprehensive examinations and the Post-CC OSCE; and 6) developed a rich sense of human nature, ethics, and scientific ability, as explained below.
1 Human Nature, Medical Ethics and Professionalism
Students will have cultivated a rich sense of human nature that is suitable to a physician, will recognize their responsibility to the profession, and will be able to contribute to society with a sense of morality, responsibility and commitment.
2 Medical Knowledge and Skills
Students will have mastered the basic knowledge and skills related to basic medicine, social medicine and clinical medicine, in order to perform medical duties, and will be able to utilize such knowledge and skills for disease prevention, diagnostic treatment and medical research.
3 Knowledge and Skills for Occupational Medicine
Students will have understood both the mission of occupational medicine and the significance of occupational health, and will have acquired and be able to use specialized knowledge and skills required for a physician to take a central leadership role in the research fields of occupational medicine and in the practice of occupational health.
4 Appropriate Capability to Support Patients and Workers
Students will have developed the mindset and attitude of a reliable physician, and will be able to respond appropriately to patients and workers, in mutual understanding, trustworthiness and full respect of their dignity and will. They will also have acquired specialized knowledge related to the support of both medical treatment and occupational life, and will be able to exercise appropriate and comprehensive judgment about disease prevention, diagnostic treatment and social reintegration.
5 Scientific Inquiry and Problem-Solving Capability
Students will have understood the significance of research in medical science and occupational health medicine, and will have acquired the scientific power of observation, thinking and expressiveness, a will to continue lifelong training, and problem-solving capabilities.
6 Communication Ability
Students will be able to establish good relations with patients, workers and other related people, appropriately exchange and share information, and give clear explanations. They will also be able to build a trusting relationship with other medical professionals and act as a member of medical teams.
7 International Health
Students will have developed an international perspective and will be able to contribute to international health in the field of occupational medicine in the future.


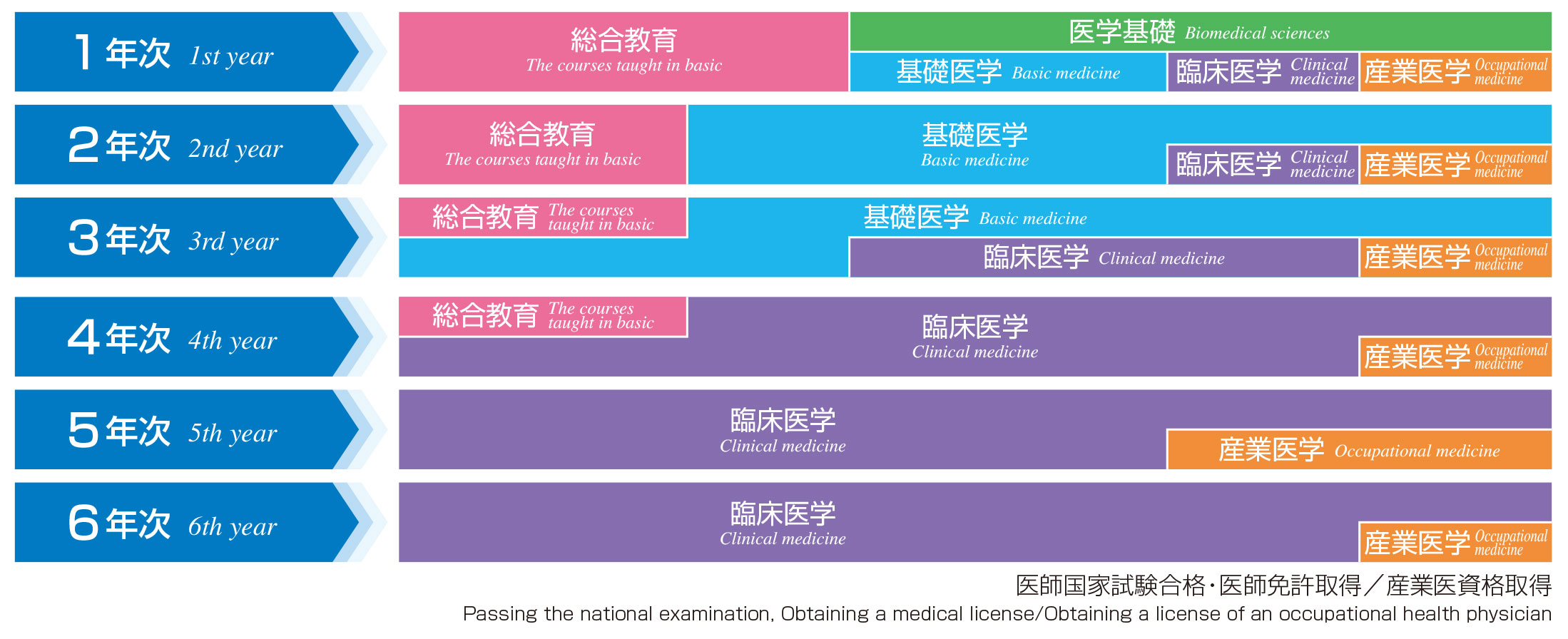
◆ Curriculum Policy
The
Department
of
Medicine,
Faculty
of
Medicine,
the
University
of
Occupational
and
Environmental
Health,
Japan,
trains
not
only
occupational
health
physicians
with
a
rich
sense
of
human
nature
and
with
a
broad
perspective
to
consider
medical
science
in
the
industrial
society,
but
also
medical
doctors
who
can
contribute
to
the
further
development
of
occupational
health
and
occupational
medicine.
To
achieve
these
goals,
we
organize
and
implement
the
following
educational
curriculum
that
is
composed
of
a
medical
education
program
that
is
consistent
with
the
Model
Core
Curriculum
in
Undergraduate
Medical
Education,
the
occupational
health
education
program
that
is
unique
to
our
university,
humanities
and
social
sciences,
medical
humanities,
and
a
special
biomedical
research
program.
|
1 |
The
Courses
in
Basic
Sciences |
| 2 |
The
Courses
in
Basic
Biomedical
Sciences These courses are designed to be integrated with each other as well as with courses in clinical medicine, to provide students with expertise required for clinical medicine, and to foster basic academic skills. The special biomedical research program gives students opportunities to cultivate various abilities such as scientific thinking, self-directed learning, problem solving, and scientific thinking and the scientific method, and to present their research findings. |
| 3 |
The
Courses
in
Clinical
Medical
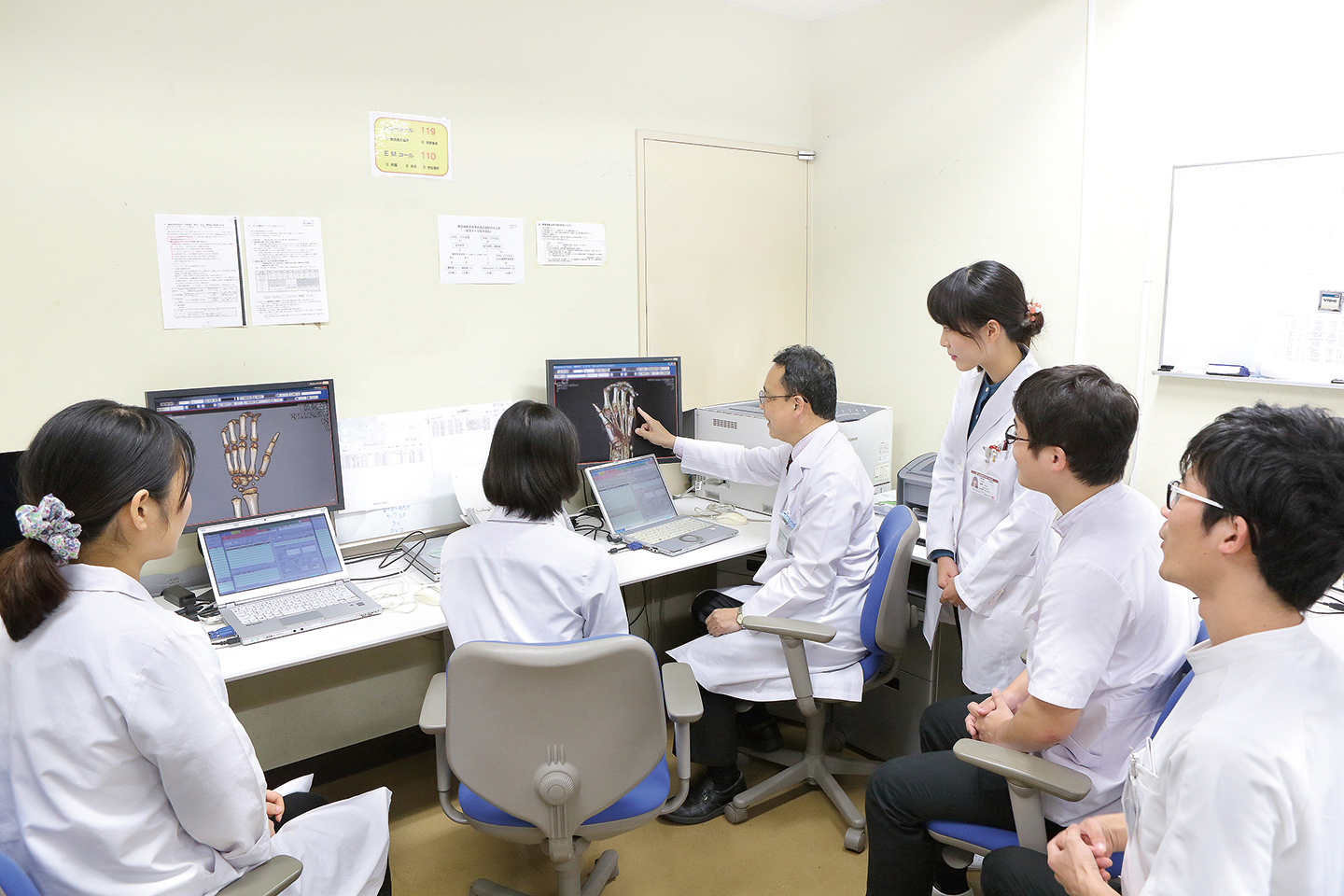
Sciences These courses are designed to have students learn the importance of mutual understanding with patients through lectures and practicums, to gain a systematic understanding of diseases and conditions, and to have basic knowledge, skills and attitude in clinical practice. Students in the upper years, who have experienced the early clinical exposure program annually since the first year, experience not only clinical practice at the university hospital, which is in collaboration with all the clinical departments, but also clinical clerkship at the university hospital and affiliated hospitals, in order to deepen their clinical knowledge and to acquire practical skills and clinical reasoning ability. They also have opportunities to experience clinical practice with foreign medical students through a mutual exchange program, to broaden their international awareness. |
| 4 |
The
Courses
in
Occupational
Medicine |
| 5 |
Small-Group
and
Interactive
Education Small classes to promote interactive education are actively implemented to foster students’ ability to solve problems, to think logically, and to communicate with others. |
| 6 |
Assessment
of
Academic
Achievement A basic comprehensive examination is administered at then end of the first, second, and third years to evaluate student’s learning achievement in each grade. Common examinations (OSCE and CBT) are administered in the fourth year, a comprehensive examination (2) is administered in the fifth year, and an integrated lecture examination concerning semeiography plus comprehensive examinations (1 and 2) and Post-CC OSCE are administered in the sixth year. |

 Request
for
documents
Request
for
documents